Anyone who lives with cats knows that cat pee has a powerful smell that is hard to ignore. Whether it’s from the litter box, a spraying incident, or an unexpected accident, the odor lingers — sometimes longer than we’d like. But the real question many people ask is: can cat pee affect your health?
The short answer is yes, it can, but usually only in specific circumstances and with prolonged or intense exposure. This guide explains how cat pee impacts your health, what makes it smell so strong, how exposure happens, and the safest way to manage and prevent issues around your home.
Let’s break it down in a simple, practical, and helpful way.
What Exactly Is in Cat Pee?
Cat pee may look harmless, but the components inside it are strong and concentrated. It contains:
- Urea
- Uric acid
- Creatinine
- Ammonia (released as pee breaks down)
- Proteins and pheromones
- Hormonal markers
- Bacteria (depending on the environment)
When cat pee sits for a while, especially in a warm or enclosed space, it becomes even stronger due to chemical breakdown — this is what creates that intense, lingering smell.
Can Cat Pee Affect Your Health?
Yes, but the level of impact depends on:
- How often you are exposed
- How strong the odor is
- How well-ventilated the area is
- Whether the pee is fresh or dried
- Whether your cat has an infection
Most people experience only irritation, but certain groups may be more sensitive.
Below are the main ways cat pee can affect your health.
1. Breathing Cat Pee Smell Can Cause Irritation
When cat pee breaks down, it releases ammonia, which has a sharp, strong odor.
Breathing in ammonia from cat pee may cause:
- Sore throat
- Coughing
- Watery eyes
- Nasal irritation
- Headaches
- Light dizziness
These symptoms are more common in small, closed areas where the pee has accumulated.
People with asthma or breathing sensitivities may react more strongly.
2. Skin Contact Can Cause Mild Irritation
Touching cat pee directly can cause:
- Redness
- Slight itching
- Minimal irritation
This usually happens when:
- Cleaning accidents without gloves
- Handling a soiled bed or surface
- Touching dried pee unknowingly
Washing your hands immediately prevents further irritation.
3. Strong Odor Can Trigger Allergies
For people allergic to cats, exposure to:
- Dander
- Saliva
- Proteins in cat pee
…may cause allergy symptoms, including:
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Skin irritation
- Itchy eyes
Sometimes people confuse allergy symptoms with “getting sick” from pee, but it’s usually an allergic response.
4. Dried Cat Pee Can Hold Odor and Bacteria
Fresh cat pee is usually less risky.
But dried cat pee can:
- Trap bacteria in carpets and fabrics
- Produce ongoing odor
- Attract mold if moisture remains
- Release odor particles back into the air
While this usually isn’t dangerous, it can be unpleasant and irritating.
5. Long-Term Exposure in Poorly Maintained Areas
Prolonged exposure to strong-smelling cat pee—like in a room with multiple accidents or an uncleaned litter box—may cause:
- Persistent headaches
- Breathing discomfort
- Strong eye irritation
- Fatigue (from poor air quality)
- Stress from overwhelming odor
These issues are more environmental than toxic — meaning the smell itself creates discomfort.
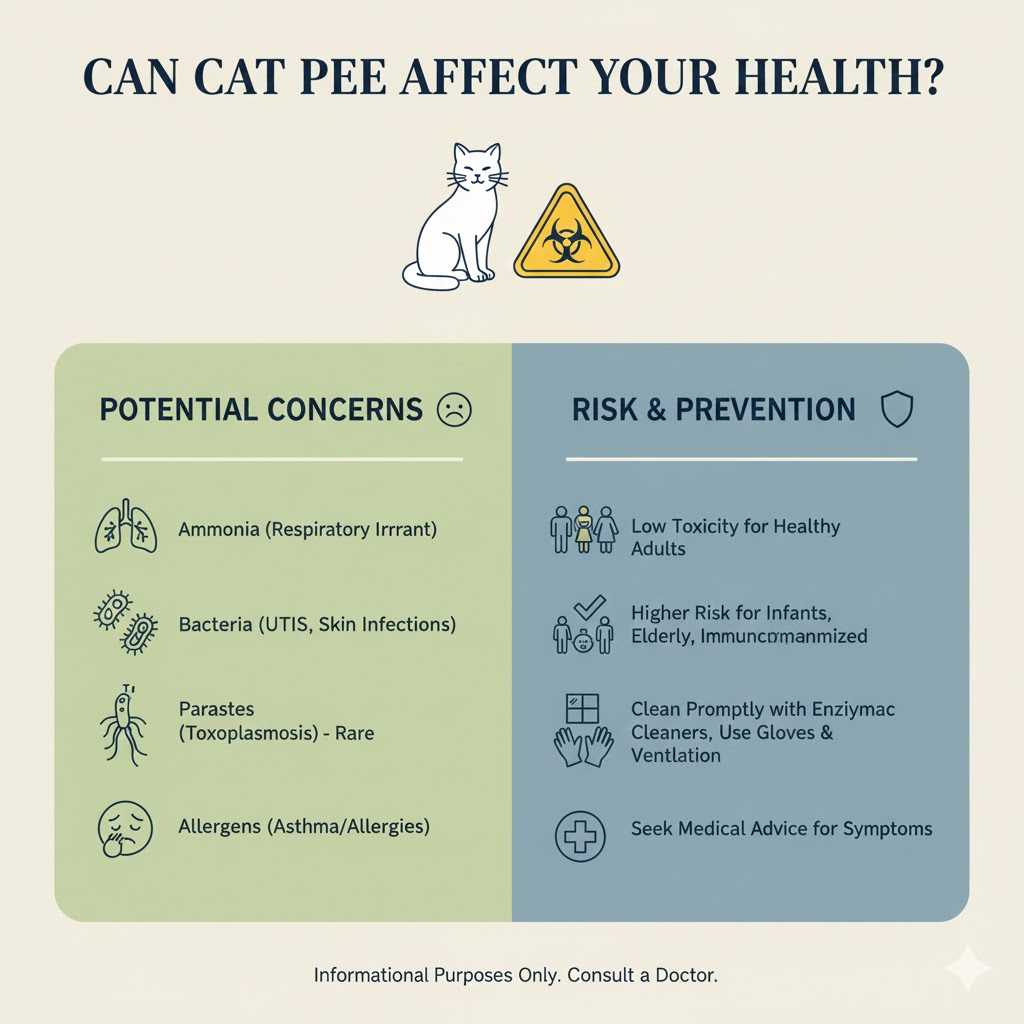
Who Is Most Affected by Cat Pee Exposure?
While many people experience only mild irritation, certain groups may be more sensitive:
- People with asthma
- Children
- Older adults
- People with allergies
- Individuals with respiratory conditions
For these groups, keeping the environment clean and well-ventilated is especially important.
Why Does Cat Pee Smell So Strong?
There are a few reasons cat pee has such a potent smell:
1. Urea breaks down into ammonia.
As soon as cat pee dries, urea converts into ammonia, making the smell more intense.
2. Uric acid binds to surfaces.
This is why the smell remains even after regular cleaning.
3. Hormones enhance odor.
Unneutered cats often produce pee with stronger scent markers.
4. Concentrated pee.
Cats naturally conserve water, resulting in more concentrated pee.
5. Aging pee becomes stronger.
Old pee becomes more pungent as it continues to break down.
Can Breathing Cat Pee Cause Long-Term Health Issues?
Normal household exposure, such as cleaning a litter box daily, does not cause long-term issues.
Problems only arise from:
- Repeated exposure to very strong odors
- Living with heavy, uncleaned pee build-up
- Not ventilating pee-affected areas
- Not removing soaked materials
These situations may lead to chronic irritation, but they are preventable with basic cleaning.
Can Cat Pee Make You Sick?
In everyday home conditions, cat pee rarely causes illness.
However, it can contribute to discomfort or irritation when exposure is high or prolonged.
The biggest concern is air quality, not toxicity.
How to Clean Cat Pee Safely and Completely
Cleaning cat pee the right way prevents odor, bacteria, and irritation.
Step 1: Blot the fresh pee
Absorb as much as possible using paper towels.
Step 2: Use an enzymatic cleaner
Enzymatic cleaners are designed to break down uric acid crystals.
Step 3: Avoid cleaners that react with ammonia
Bleach + ammonia = unsafe combination.
Step 4: Rinse and dry
Repeat until the smell disappears.
Step 5: Ventilate the room
Open windows, turn on fans, circulate fresh air.
Step 6: Replace heavily soaked materials
If the pee has penetrated deep layers (pads, wood, or flooring), replacement may be required.
How to Remove Cat Pee Smell from Different Surfaces
Carpet
Use an enzymatic cleaner and saturate deep into the padding.
Mattress
Blot, saturate with enzymatic cleaner, then allow extended drying time.
Clothes
Wash with enzymatic laundry booster.
Furniture
Use pet-safe cleaners designed for fabrics.
Hard Floors
Wipe with mild cleaner + enzyme spray.
Signs Your Cat Is Peeing Outside the Box
If accidents are frequent, it may signal:
Medical issues
- Urinary discomfort
- Stress-related bladder problems
- Dehydration
- Pain while urinating
Litter box issues
- Dirty box
- Wrong litter type
- Small or enclosed box
- Box in a noisy or inaccessible location
Behavioral reasons
- Stress
- Territorial marking
- Changes in the home
Addressing the cause prevents future exposure.
How to Prevent Cat Pee Odor and Health Issues
- Scoop the litter box daily
- Wash the box weekly
- Use a high-quality litter
- Provide one box per cat, plus one extra
- Keep the home ventilated
- Clean accidents immediately
- Reduce stress triggers for your cat
Simple habits go a long way in preventing odor and exposure.
Is Cat Pee Dangerous for Babies or Pets?
Cat pee around babies or other pets is not inherently dangerous, but exposure should be minimized:
- Babies may touch contaminated surfaces
- Pets may walk through or sniff old spots
- Strong smells can irritate sensitive noses
A clean, fresh environment is the best protection.
Read Also : How Much Is a Health Certificate for a Cat
Conclusion
Cat pee can affect your health, but mainly through irritation, strong odors, and poor air quality in cases where accidents are not cleaned properly. In everyday situations with regular cleaning and ventilation, the risk is low.
If odor issues are persistent or your cat is having frequent accidents, addressing the root cause—whether environmental, behavioral, or medical—will improve both your health and your cat’s well-being.
Living with cats can be clean, safe, and comfortable with the right habits and care.
FAQs
1. Can smelling cat pee be harmful?
Strong odors can irritate your eyes, nose, or throat, especially in small, unventilated spaces.
2. Is dried cat pee worse than fresh pee?
Yes. Dried cat pee becomes more concentrated and harder to remove.
3. Can cat pee cause headaches?
Strong ammonia smell can trigger headaches in some people.
4. Is touching cat pee dangerous?
Direct contact can irritate skin but washing with soap removes risk.
5. Why does my house smell like cat pee even after cleaning?
Uric acid can remain trapped in carpet padding, wood, or fabrics if not cleaned with enzymatic products.
