When a cat suddenly refuses food, it can be frightening for any pet owner. Cats are known for being picky eaters, but when they go too long without eating, it becomes more than just a mood or preference. Understanding how long can a cat go without eating — and what warning signs to watch for — can protect your cat’s health and help you take action fast.
In this guide, you’ll learn how long can a cat go without eating, why they stop eating, what happens to their body during hunger, and what you should do immediately if your cat is avoiding food.
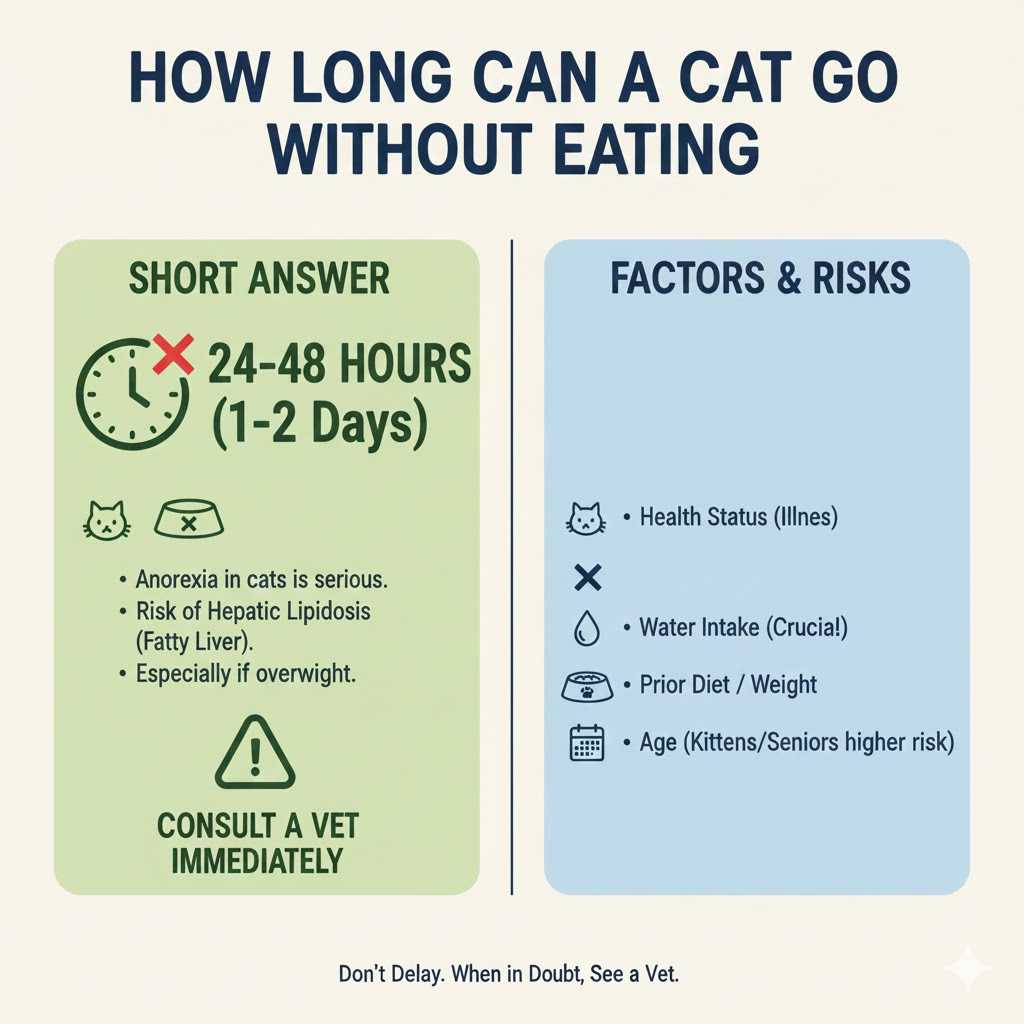
How Long Can a Cat Go Without Eating?
Most healthy cats can go 24 to 48 hours without eating, but anything beyond that is risky.
If a cat goes more than 72 hours without food, it may develop fatty liver syndrome, a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
Safe General Timeline:
- 0–24 hours: Usually safe, but unusual if your cat loves food.
- 24–48 hours: Concerning; monitor closely and try appetite-boosting steps.
- 48–72 hours: Dangerous territory — a vet visit is strongly advised.
- Over 72 hours: The risk of severe organ damage rises sharply.
Cats do not handle fasting like humans or even dogs. Their bodies depend on steady food intake to metabolize fat properly.
Why Cats Can’t Go Long Without Eating
Cats are obligate carnivores, which means their bodies rely heavily on protein and fat for energy. When they stop eating, their body begins breaking down stored fat. But without enough protein, the liver struggles to process this fat, leading to fat accumulation.
This condition is known as feline hepatic lipidosis (often called “fatty liver”). It can develop quickly and become deadly if not treated early.
Key reasons why cats decline faster without food:
- Their metabolism is designed for regular meals.
- Their livers cannot process fat efficiently.
- Their bodies need constant protein intake.
- Prolonged hunger triggers stress and worsens illness.
Why Has My Cat Stopped Eating?
There are many possible causes for appetite loss. Some are mild and temporary, while others require urgent care.
Below are the most common reasons cats stop eating:
1. Stress or Environmental Changes
Cats are creatures of habit. Even small changes can throw them off.
Common stressors:
- Moving to a new home
- New pets or people
- Loud noises
- Rearranging furniture
- Traveling
- Vet visits
- Change in their food brand
Stress or anxiety is one of the most common and overlooked causes of sudden appetite loss.
2. Dental or Mouth Problems
If eating causes pain, a cat may refuse food entirely.
Possible dental issues include:
- Tooth decay
- Gum inflammation
- Abscesses
- Mouth ulcers
- Broken or loose teeth
Cats often hide mouth pain, so appetite loss may be the first clue.
3. Illness or Infection
Many health conditions directly affect appetite.
Some common examples include:
- Fever
- Kidney issues
- Digestive problems
- Respiratory infections
- Pancreatitis
- Thyroid imbalance
Any illness can make a cat feel too weak or nauseous to eat.
4. Nausea or Stomach Upset
If your cat feels queasy, they may sniff food but walk away.
Common causes:
- Eating something unusual
- Hairballs
- Worms
- Food intolerance
- Gastritis
A cat that’s nauseous may also drool or hide.
5. Dehydration
Cats often avoid drinking enough water, and dehydration can suppress appetite.
Reasons for dehydration:
- Heat
- Illness
- Stress
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
Without hydration, appetite loss worsens.
6. Pain or Discomfort
Cats may stop eating when they experience:
- Joint pain
- Abdominal discomfort
- Injuries
- Internal inflammation
Cats are subtle about pain, so appetite decline may be the main sign.
7. Food Preferences
Cats may reject food if:
- You changed the flavor or brand
- The food is stale
- The texture is off
- The bowl smells like soap or chemicals
- They dislike wet or dry food options
Sometimes the solution is as simple as switching flavors.
Signs Your Cat Is Not Eating Enough
Along with reduced food intake, you may notice:
- Weight loss
- Lethargy
- Hiding behavior
- Dehydration
- Vomiting or drooling
- Less grooming
- Smelly breath
- Weakness
- Sunken eyes
These symptoms indicate that your cat needs help promptly.
What Happens If a Cat Doesn’t Eat?
Lack of food affects cats quicker than many owners expect.
Within 24–48 hours:
- Energy drops
- Mild dehydration begins
- Mood changes
Within 72 hours:
- Fat breakdown overwhelms the liver
- Fatty liver syndrome may begin
- Jaundice (yellowing of ears, gums, or eyes) can appear
- Nausea increases
- Organ stress starts
After 3 days without food:
This is an emergency.
The body begins shutting down essential functions.
What To Do if Your Cat Isn’t Eating
You can try several steps at home before seeking medical care, but you should always act quickly.
1. Try Warming the Food
Heating wet food slightly can make it more aromatic and appealing.
2. Offer a Strong-Smelling Food
Options include:
- Tuna juice
- Plain cooked chicken
- Smelly wet food flavors
A sudden burst of smell can re-trigger appetite.
3. Change the Feeding Environment
Make sure:
- The area is quiet
- No other pets are intimidating
- The food bowl is clean
- The room isn’t too hot or cold
A relaxed space encourages eating.
4. Add a Small Amount of Broth
Unsalted broth added to food increases flavor and moisture.
5. Try Hand-Feeding
Some cats eat more willingly when hand-fed during stress or recovery.
6. Ensure Fresh Water
Hydration often helps encourage appetite.
7. Test Different Textures
Some cats prefer:
- Pâté
- Shredded meat
- Dry kibble
- Soft morsels
Experiment to see what your cat prefers.
8. Address Stress Triggers
If something changed recently, try returning to your cat’s normal routine.
Provide:
- Safe hiding spots
- Comforting objects
- Calm atmosphere
When to See a Vet
Seek professional help immediately if:
- Your cat has not eaten for over 24 hours
- Your cat is also vomiting or has diarrhea
- Your cat seems weak or dehydrated
- Your cat is elderly or has medical conditions
- You notice yellowing eyes, gums, or ears
- Your cat refuses even favorite foods
A vet can diagnose the underlying problem and may provide:
- Appetite stimulants
- Fluids
- Pain relief
- Anti-nausea medication
- Dental treatment
- Blood tests or imaging
Early intervention prevents complications.
How to Prevent Appetite Loss in the Future
You can reduce the chances of sudden food refusal by keeping your cat’s routine stable.
Helpful preventive steps:
- Always provide fresh food and water
- Keep bowls clean
- Avoid frequent food changes
- Maintain regular feeding times
- Reduce stress
- Create a calm eating spot
- Brush your cat regularly to prevent hairballs
- Monitor any emotional or behavioral changes
Prevention is easier than emergency treatment.
Common Myths About Cats and Eating
Let’s clear up some misunderstandings:
Myth 1: Cats can fast like humans.
False.
Even short fasting can harm them.
Myth 2: “My cat will eat when they are hungry enough.”
False.
Some cats will starve rather than eat when stressed or ill.
Myth 3: Dry food is enough even if they skip wet food.
Not always.
Cats need consistent nutrition from the type of food they prefer.
Myth 4: Losing weight quickly is normal.
False.
Rapid weight loss is a red flag.
How Long Can a Sick Cat Go Without Eating?
If a cat is sick, the safe window becomes even shorter.
A sick cat can begin experiencing complications within 24 hours.
It’s important not to “wait and see” in these cases.
How Long Can a Kitten Go Without Eating?
Kittens cannot go without food as long as adult cats.
- Young kittens: 4–6 hours
- Older kittens: 6–12 hours
Kittens have small stomachs and fast metabolisms, so skipping meals is dangerous.
Read Also : Why Won’t My Cat Stop Meowing
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Should I force-feed my cat if it’s not eating?
No. Force-feeding may cause stress or choking. Seek guidance from a professional if your cat hasn’t eaten for over 24 hours.
2. What if my cat refuses both wet and dry food?
Try offering a different flavor, warming the food, or adding broth. If refusal continues, get professional help.
3. Can picky eating be a long-term behavior?
Yes, some cats are naturally selective, but persistent food refusal isn’t normal.
4. Can stress cause a cat to stop eating?
Yes, stress is one of the most common reasons cats temporarily stop eating.
5. Should I change food brands if my cat stops eating?
Sometimes a switch helps, but sudden changes can backfire. Introduce new foods gradually when possible.
Conclusion
Cats are sensitive creatures, and going without food can quickly turn dangerous. While a short period of reduced appetite might not be alarming, going without food for more than 24–48 hours can lead to serious health risks. Understanding the causes, acting quickly, and knowing when to seek help can protect your cat’s well-being.
If your cat stops eating, trust your instincts — early action can make all the difference.
